Anchor Initialization
This tool will visualize the results of the anchor's initialization that was previously done in the RTLS Manager, so you can easily see and evaluate its results. You can use this tool for correct master selection. Further information about the Procedure for Master Selection is described in the Project Delivery section.
Known Issue
Due to the latest browsers update GUI components in RTLS Studio 2.4 and lower start to be incompatible. Fix and more details you can find in section Known Issues.
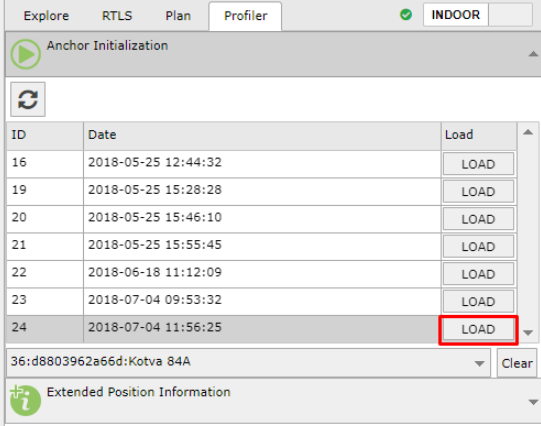
To view the results, simply load the latest initialization that was performed. It can be selected by using the "Load" button:
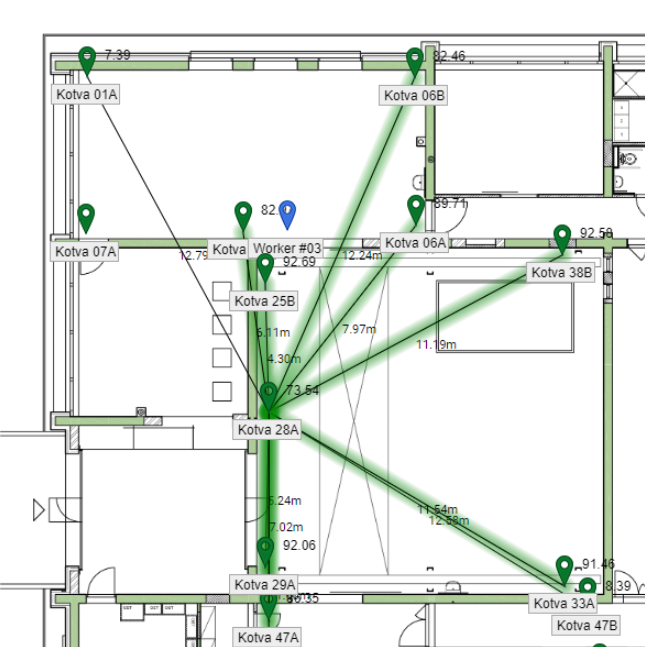
Then click on the anchor in the plan, for which you want to reveal the extended initialization information.
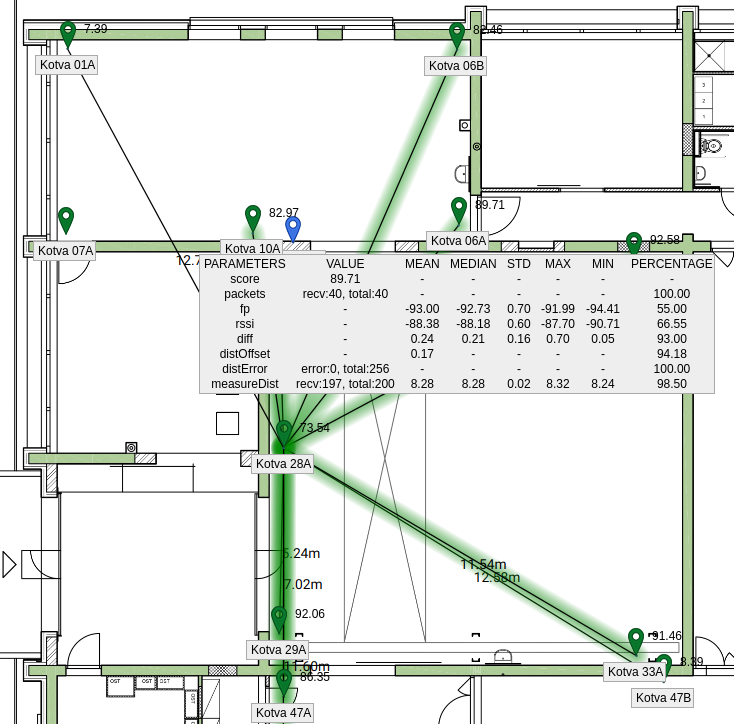
If you would like to see more details please hover mouse over slaves, tooltip will appear with detailed information about measurements
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| score | Overall quality of slave for given master, which is evaluated from all metrics (packets, fp, rssi, diff, distOffset, distError, measureDist) | 100 is best slave possible, 0 worst. Usable slaves usually have scores above 70, but score above 85 is preferable |
| packets | Each master is evaluated by transmitting 40 packets which are being received by slaves | Slave should receive at least 90% of packets transmitted by master, i.e. 36 packets out of 40 |
| fp | Metric First Path denotes the quality of received signal. Similar to RSSI, but FP is more sensitive to reflections (non-line-of-sight). | -75 is best value (but never reached in practice because the value lowers with increasing distance), -115 is worst value, however in some cases still usable. One should be aware if there is variance in this metric, e.g. first path frequently drops from -97 to -110 |
| rssi | Metric RSSI (received signal strength indicator) indicates power in received signal | -75 is best value, -115 worst value. RSSI has usually slightly better values than FP |
| diff | Metric diff denotes second difference which indicates stability of synchronization | This value should stay below 2 (MEDIAN) with low STD |
| distOffset | During initialization master anchor acts as tag and therefore other slaves might try to localize it. This metric shows how real position (input by user in Sensmap) differs from the "localized" position. This metric can be evaluated only if anchors are already placed in Sensmap. | Value is in meters, the lower the better. Value N/A means that metric cannot be evaluated (probably because anchors are not placed in Sensmap) |
| distError | Metric associated with distOffset - sometimes the "localized" position cannot be determined due to error in measurements. This metric says how often that happens. Again, can only be evaluated if anchors are already placed in Sensmap | total value is total number of computations and error is number of failed computations. The lower, the better. Value N/A means that metric cannot be evaluated (probably because anchors are not placed in Sensmap) |
| measureDist | Anchor Auto Deployment enables calculation of distance between slave and master. During initialization this calculation is performed 200 times. | The numbers show distance in meters between given master and slave. The number should be as close as possible to a distance which is calculated from anchors' position input by user (this distance can be seen next to line between master and slave). One should be aware if these two distances are significantly different (more than 30cm), this could mean that anchors are placed incorrectly, anchors communicate in reflections or in NLOS conditions and restrictions should be therefore considered. |