Device Care History
The Device Care History section provides an enhanced view of your system’s data, allowing you to analyze metrics over time and in more detailed graphs. This section not only extends the data from a time-based perspective but also displays the metric data in more complex and informative charts.
To begin, you must define the desired time range. Use the Visible Range dropdown to select the time period you wish to review. This will determine the scope of the historical data displayed.
You have the option to filter the data using the Show Alerting Only checkbox. When this checkbox is selected, the view will display only the data related to alerts triggered by the thresholds you've set. If the checkbox is unchecked, the system will display all available data for the chosen time period, regardless of alert status.
Once you’ve specified the time period, you can access the historical data related to various components of the RTLS system, such as Anchors, System Performance, RTLS Studio, and Tags. This section allows you to drill down into the specifics of each metric and analyze past performance or issues in greater detail.
The following sections will further explain the graphs and metrics associated with each system component.
Anchors
This section provides a real-time overview of anchor connectivity and localization cell synchronization status in your RTLS system.
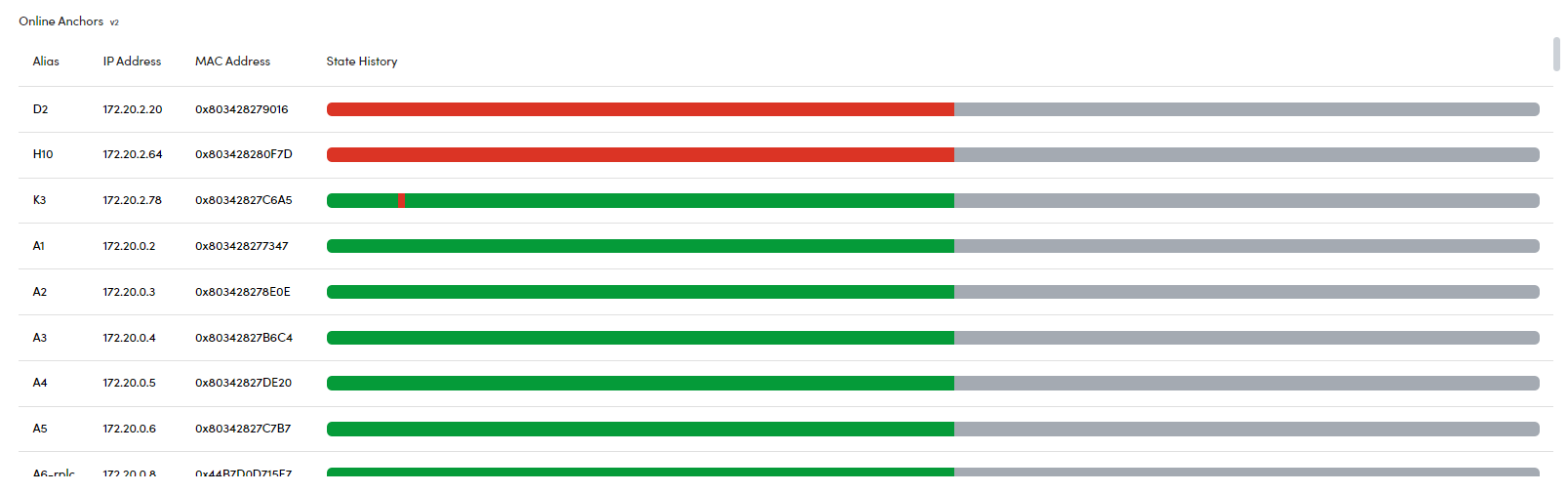
Online Anchors
This metric displays the current status of each anchor connected to your RTLS system, indicating whether it is Online or Offline. The table provides the following details for each anchor:
- Alias: The custom name or identifier for each anchor.
- IP Address: The anchor's assigned IP address within the network.
- MAC Address: The unique hardware identifier for each anchor.
- State History: A horizontal progress bar showing the anchor's status over time.
Each anchor can have one of the following states:
- Online (Green): The anchor is actively communicating with the server, indicating proper functionality.
- Offline (Red): The connection to the anchor has been lost, and it is not currently communicating with the server.
The State History bar provides a visual representation of the anchor's status over time. A continuous green bar indicates stable connectivity, while sections of red show periods when the anchor was offline. This allows you to monitor the health of each anchor over a selected period and quickly identify any connectivity issues.
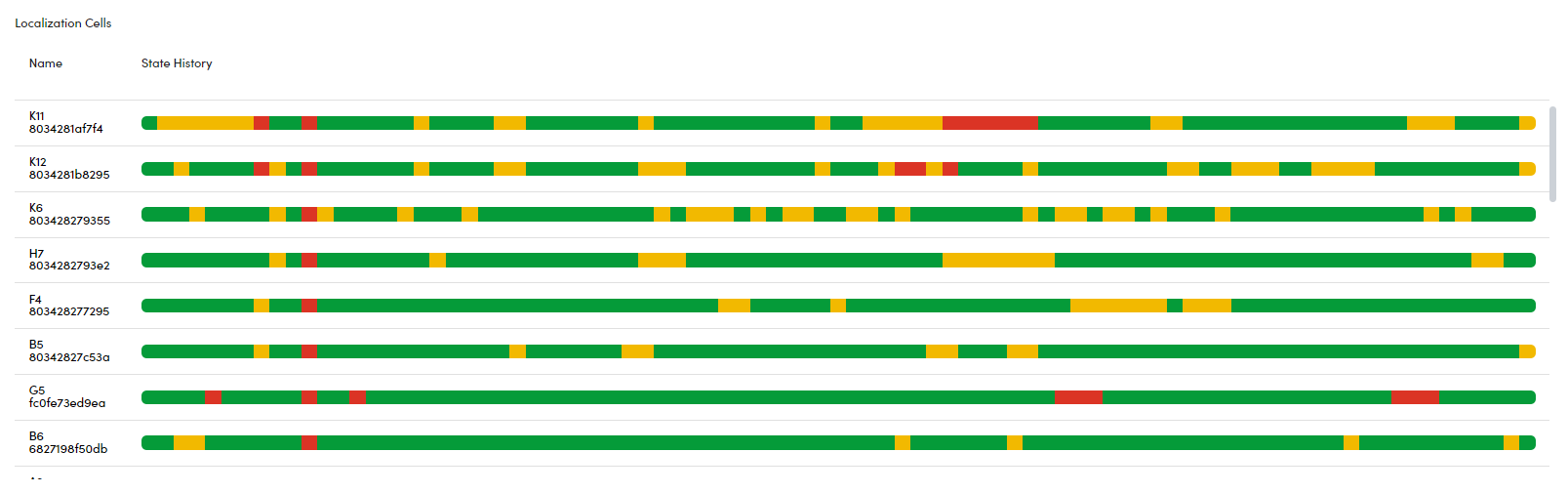
Localization Cells RETIRING
This graph provides an overview of the synchronization status for each master within your RTLS system. The list of masters is displayed on the left side, and for each master, the graph indicates whether its corresponding localization cell is properly synchronized and actively contributing to localization performance.
The state of each localization cell is crucial because synchronization issues can significantly affect the accuracy and efficiency of localization. The possible states are:
OK (Green): The localization cell is fully operational and contributing to accurate localization. If the cell doesn't have enough anchors due to restrictions, it may act as a bridge while still functioning correctly.
WARNING (Yellow): Some anchors in this cell are not being utilized, but overall, the cell is still functional and providing sufficient localization performance.
BAD (Red): The localization cell is not being used or is performing poorly. This state indicates that synchronization issues are severely affecting the cell's ability to contribute to localization.
By monitoring this graph, you can quickly assess the health and synchronization status of each master and its impact on the overall localization performance, allowing for timely troubleshooting and adjustments as needed.
Tags
This section provides a real-time overview of tag battery statuses and inactive tags, helping you monitor battery levels and identify tags that require recharging or have been inactive for extended periods, ensuring optimal positioning.
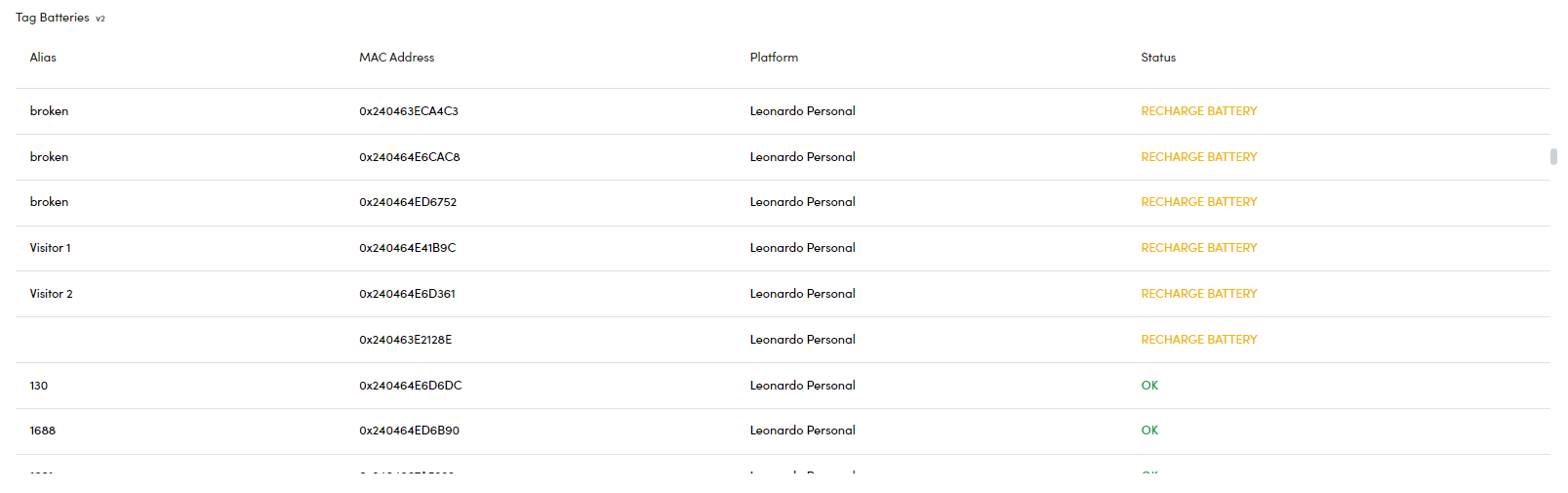
Tag Batteries
This table displays a list of all tags in your system along with the current status of their batteries. Each tag is shown with its Alias, MAC Address, Platform, and Battery Status. The status of each tag's battery can be one of the following:
CHARGED (Green): Tags with this status have sufficient battery life and can continue operating for a considerable amount of time, depending on the refresh interval and usage.
LOW BATTERY (Yellow): This status indicates that the tag's battery is low and may soon reach a critical level. If not recharged, the tag will eventually turn off due to insufficient power.
By monitoring this table, you can quickly identify which tags require battery recharging and ensure uninterrupted operation of your RTLS system.
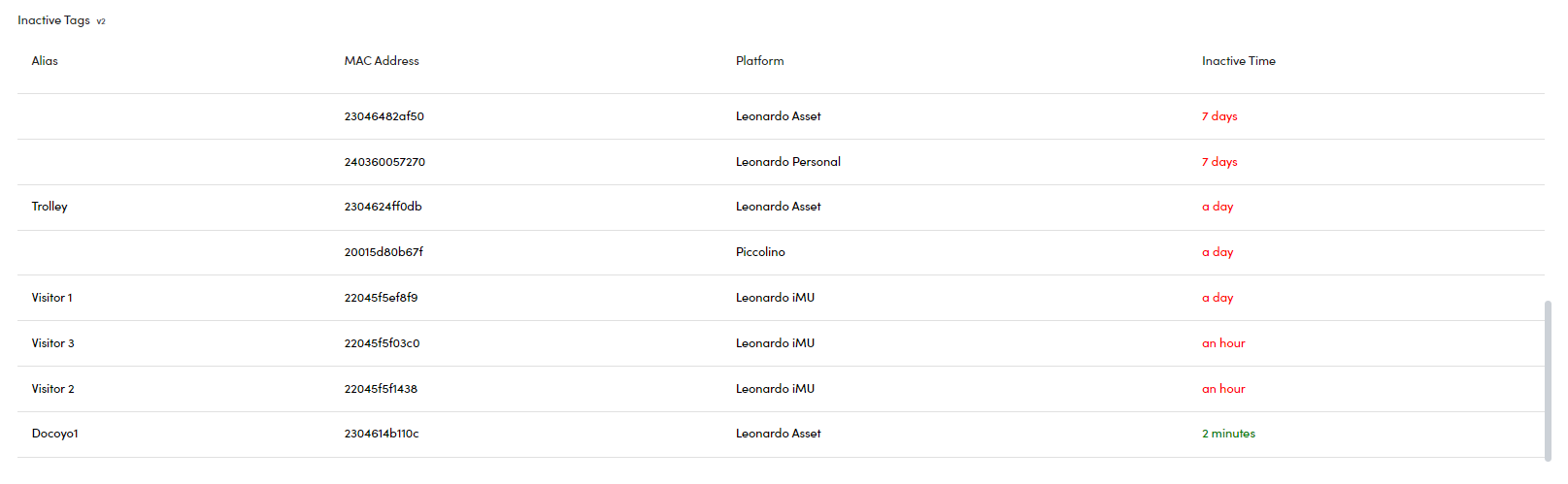
Innactive Tags BETA
This table displays a list of tags in your system that have been inactive for a specified period. Each tag is shown with its Alias, MAC Address, Platform, and the length of its Inactive Time.
Tags are considered inactive if they have not communicated with the system for a set period. The Inactive Time is color-coded:
- Green: Recently inactive (based on the threshold set in Device Care Settings).
- Red: Inactive for a longer period (e.g., hours, days, or more).
This information helps to quickly identify tags that may require maintenance, replacement, or reactivation to maintain optimal system performance.
System
This section provides an overview of system performance, including server uptime, hard drive space, RAM availability, and CPU load, with visual graphs for monitoring key metrics and triggering alerts if thresholds are exceeded to maintain optimal system operation.
Uptime
This section provides a comprehensive record of all server restarts and connectivity issues between the myRTLS cloud and RTLS server within the selected time period. For each incident, the exact date and time are displayed, offering precise insights into when the RTLS server experienced a restart or connectivity disruption. This information enables you to monitor the system’s uptime, track potential periods of downtime, and identify any maintenance activities or connectivity issues affecting system performance.
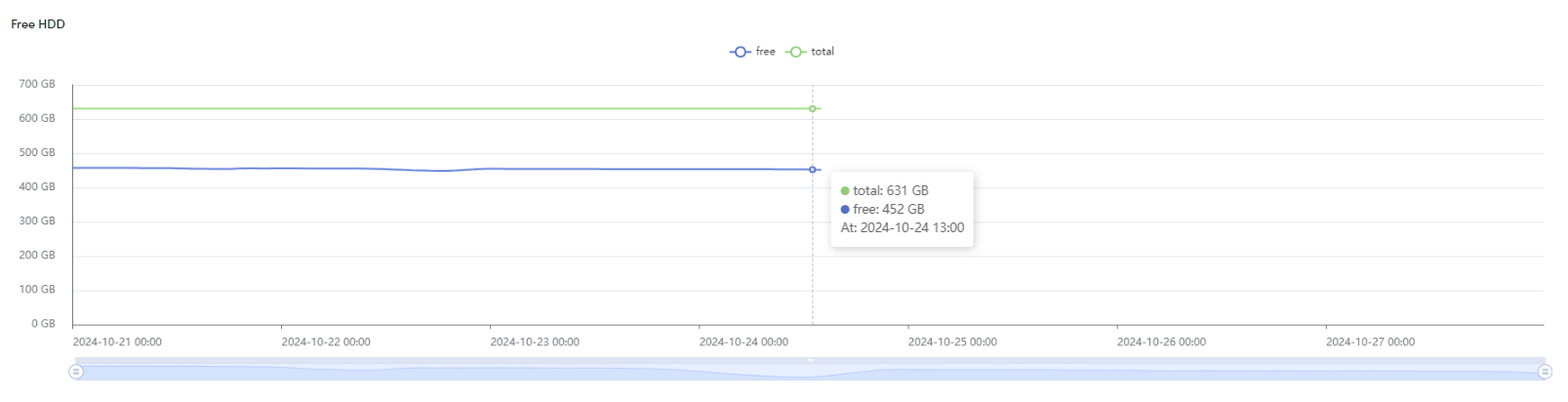
Free HDD
This graph displays the available free space on your hard drive over time. The blue line shows the current amount of free space, while the green line indicates the total capacity of the hard drive.
Monitoring this graph helps ensure your system has sufficient storage to function smoothly. If the available space falls below a predefined threshold (represented by the red area), an alert will be triggered, allowing you to take action before storage limitations impact system performance.
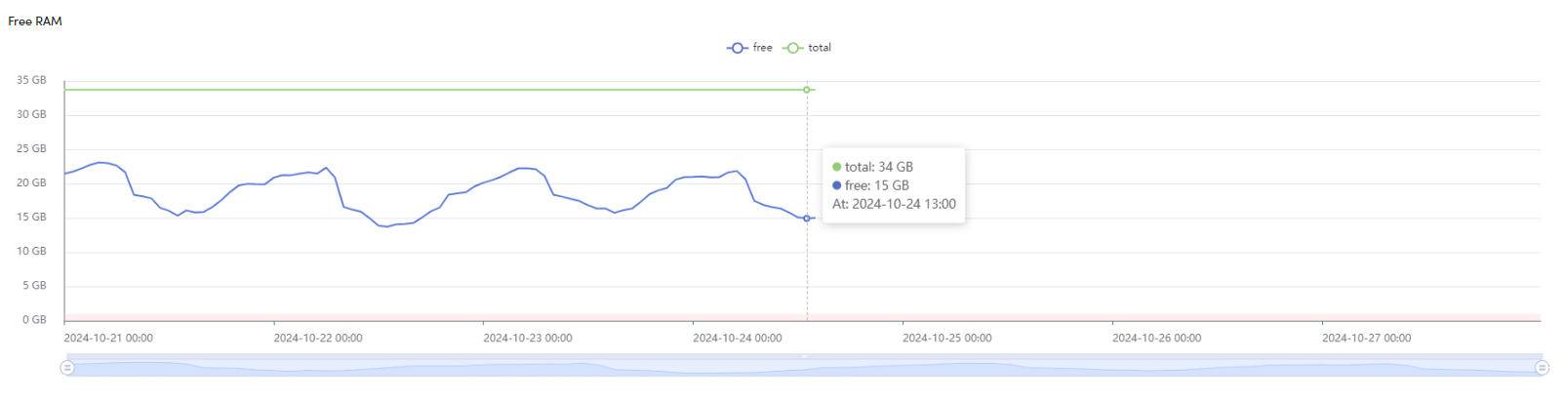
Free RAM
This graph shows the amount of free RAM available in your system over time. The blue line represents the current amount of free memory, while the green line indicates the total RAM capacity.
By monitoring this graph, you can ensure your system has enough memory available to operate efficiently. If the free memory falls below a predefined threshold (indicated by the red area), an alert will be triggered, enabling you to address memory usage issues before they affect performance.
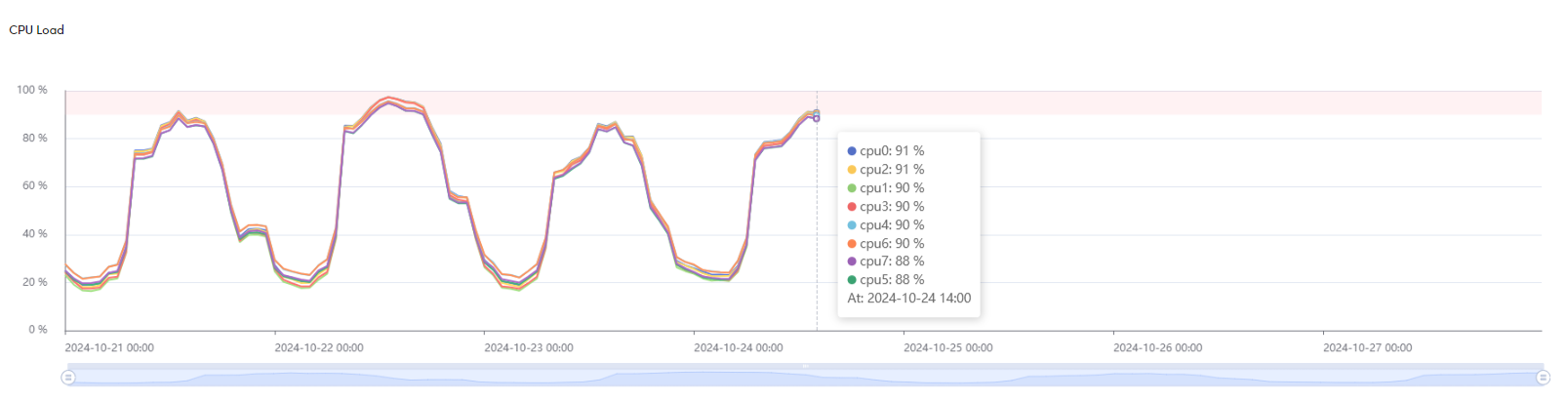
CPU Load
This graph displays the CPU utilization over time, showing the percentage of usage for each individual CPU core in the system. Each line represents the usage of a specific CPU.
If the CPU load exceeds 90% (indicated by the red area), an alert will be triggered. Monitoring this graph helps you track CPU performance and ensure that high CPU usage does not negatively affect the system's operation.
RTLS Studio
This section provides an overview of service restarts, REST API response times, and WebSocket API latency, helping to monitor system stability, API performance, and the efficiency of position calculations.
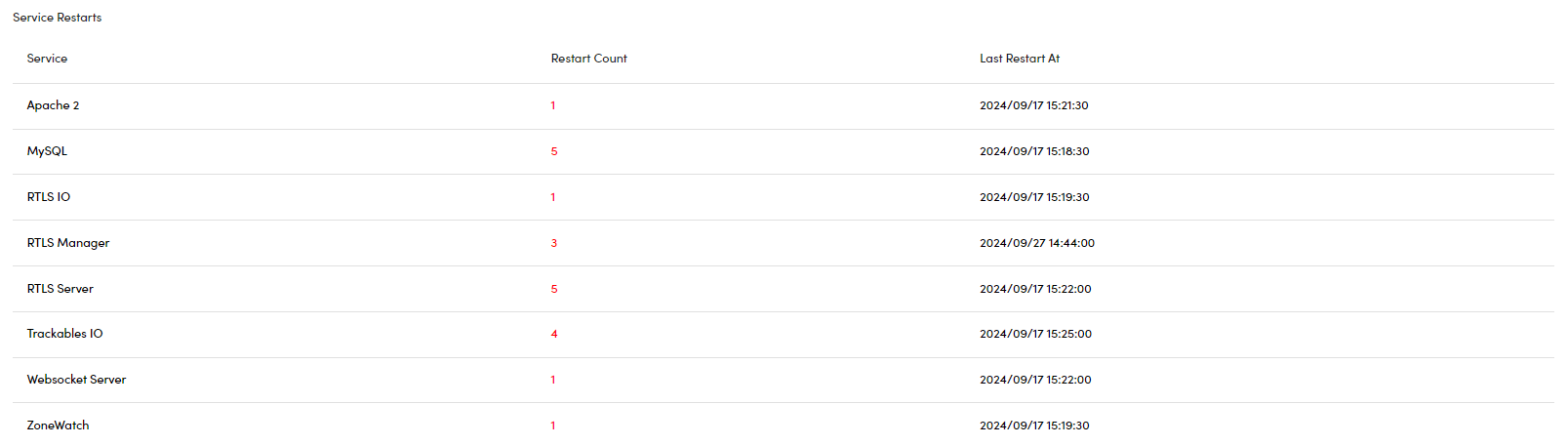
Service Restarts
This table provides a list of services that have been restarted within the selected time period. For each service, the following details are displayed:
- Service Name: The name of the service that experienced a restart.
- Restart Count: The total number of restarts for each service during the selected period.
- Last Restart At: The exact date and time of the most recent restart for each service.
This information helps track system stability by showing which services were restarted and how frequently, allowing you to monitor and troubleshoot any potential issues related to service reliability.
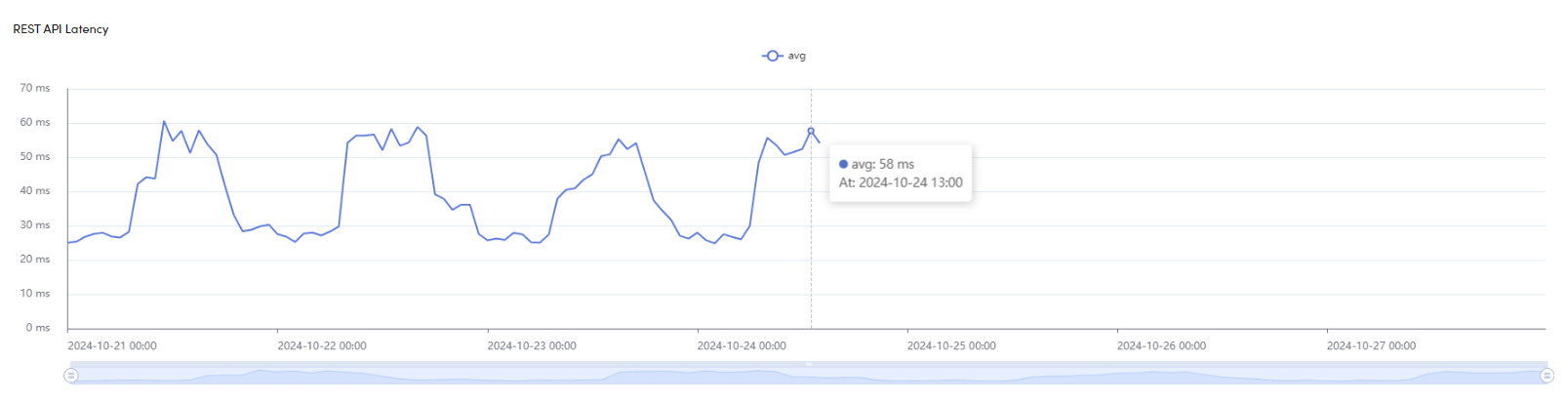
REST API Latency
This graph displays the average response time of the REST API from the server over the last minute. The blue line represents the fluctuation of the API response time in milliseconds (ms) over the selected time period. By monitoring this graph, you can assess the server's performance and identify any potential latency issues that may impact API request handling. Consistently high response times may indicate the need for further investigation into server performance.
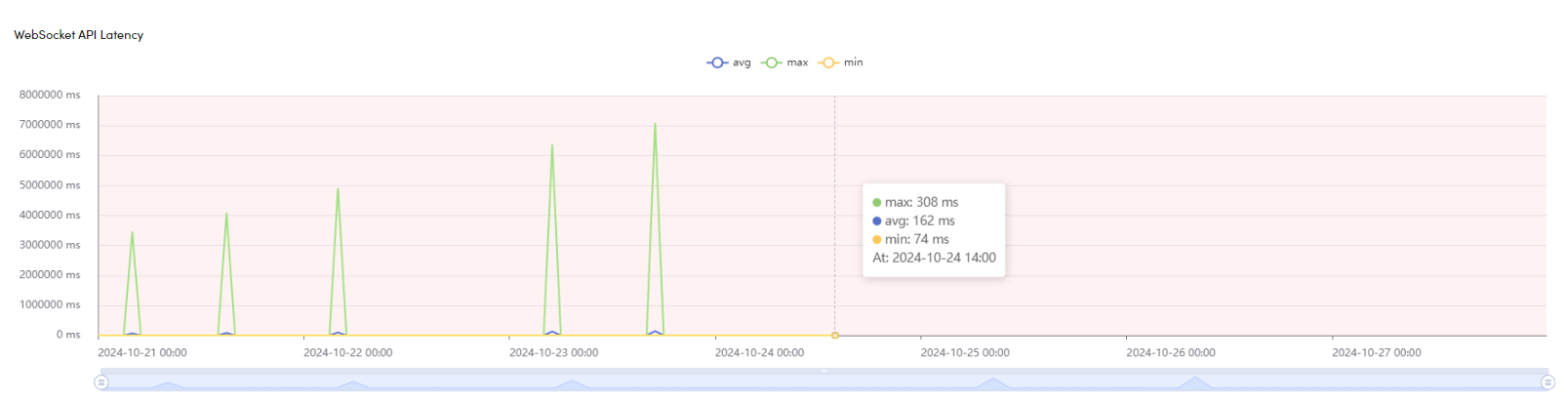
WebSocket API Latency
This graph displays the latency for position calculations over WebSocket. It shows the following metrics:
- Average (blue line): The average time taken for position calculations.
- Maximal (green line): The longest duration for a position calculation within the measured timeframe.
- Minimal (yellow line): The shortest duration for a position calculation.
The duration is measured on the server from the moment anchor messages are received until the calculated positions are sent via WebSocket API. Monitoring this graph allows you to track the performance of position calculations and identify any latency issues affecting the WebSocket communication.